Validation of the lead-in method in a practical shooting scenario
Maddie Keldson MScFS, Eugene Liscio BE
See also the instructional videos on "Using Strings and Lasers for Bullet Trajectories"
Abstract
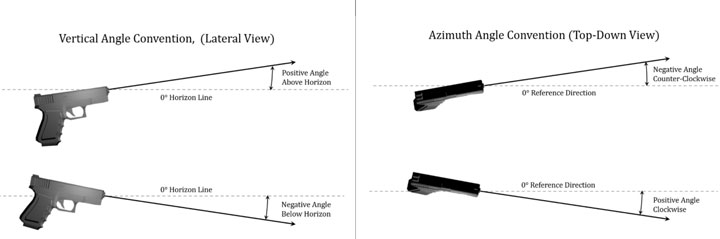
The ability to determine bullet trajectories after a shooting incident can allow investigators to reconstruct the locations of individuals and the sequence of events that took place. By using trajectory rods, investigators can be provided with an immediate visual estimate as to what the path of the projectile may have been. In certain instances, the use of the probing method with trajectory rods is not appropriate due to their being a single, thin target material, or no secondary bullet impact site. In these cases, other methods such as the lead-in or the ellipse method may be useful. Overall, the lead-in method has not been well studied in the application to practical scenarios, such as those including bullet impacts on vehicle metal surfaces. This study has explored the accuracy of the lead-in method when a bullet impacts a typical vehicle metal surface using three firearm calibers, three blind participants, and two non-blind participants. The results of this study have shown that each caliber has its own characteristic error curve. In general, it was found that the lower the impact angle, the less errors were made by the participants. As the impact angle increases, the measurement errors increased, due to the smaller lead-in area present. The errors were found to have a wide range, with some being as low as 1° and some being as high as 13.9°. Further, it was found there was no significant effect on the errors of blind versus non-blind participants.
 Highlights
Highlights
- Practical application of the lead-in method to measure single bullet impacts on car doors.
- Lower impact angles tend to have less errors when using the lead-in method.
- Identified characteristic error patterns and curves of three calibers using lead-in method.
- Knowing how a firearm-ammunition combination performs may allow to make corrections to bring values back to a more accurate answer.
Read the report:
 © 2024 The Authors. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction, provided the original work is properly cited and not changed in any way.
© 2024 The Authors. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction, provided the original work is properly cited and not changed in any way.
How to cite this article: Keldson M, Liscio E. Validation of the lead-in method in a practical shooting scenario. J Forensic Sci. 2024;69:1235–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.15523

